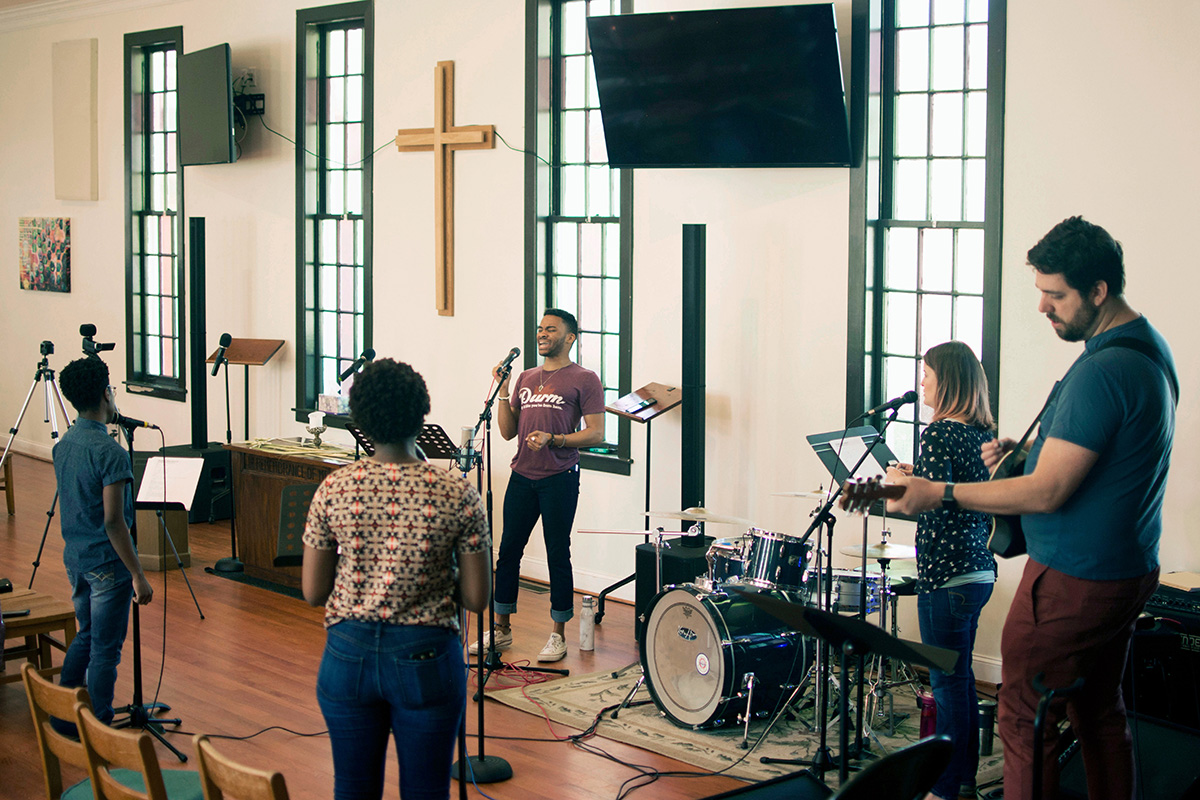About 20 years ago, the largely white Garfield Memorial United Methodist Church faced a decision: Focus on people outside the church or accept the dwindling attendance within.
“Folks started sensing, ‘Maybe we haven’t been a church. Maybe we have been a club,’” said the Rev. Chip Freed, the church’s lead pastor since 2004.
The church was in a slump. But with a renewed focus on the Great Commission and the Great Commandment, the suburban Cleveland church decided to share God’s love outside its doors — and welcome whoever responded.
In time, Garfield Memorial grew from an average attendance of about 200 middle-class white members to more than 1,000 people of varied economic backgrounds and ethnicities. Today, no one ethnic group comprises more than 52 percent of the now multi-campus congregation.
A new comprehensive study of The United Methodist Church shows Garfield Memorial Church’s experience of diversity and growth is far from unusual.
The Baylor University-led study, published in the journal Social Forces, found that racially diverse United Methodist churches are more likely to have higher worship attendance over time than their white counterparts. The research also found that white churches in nonwhite neighborhoods fare the worst in attendance.
To reach that conclusion, the study’s authors tracked local worship attendance data of more than 20,000 U.S. United Methodist congregations from 1990 to 2010. They paired that information with neighborhood data from the U.S. Census Bureau to investigate the effect of demographic change on congregations.

A multi-ethnic worship team leads music during Easter Sunday worship at Garfield Memorial United Methodist Church in suburban Cleveland, Ohio. Screenshot courtesy of Garfield Memorial United Methodist Church.
“In some ways, looking at The United Methodist Church is looking at the history of the United States and contemporary trends in race and religion,” said Kevin D. Dougherty, the study’s lead author and a sociology professor at Baylor. “It was a terrific case study for us to look at what happens in neighborhoods and churches over a block of time.”
His co-authors are fellow sociology professors Gerardo Martí of Davidson College and Todd W. Ferguson of the University of Mary Hardin-Baylor.
Gallup and church growth
The same week that Baylor University publicized a study that highlights United Methodist church growth, Gallup released its poll showing that Americans’ membership in houses of worship is continuing to decline.
Gallup found that in 2020, 47% of Americans said they belonged to a church, synagogue or mosque. That’s the first time that percentage dropped below half in Gallup’s 80-decade trend. At the same time, the number of Americans who express no religious preference continues to rise.
The Lewis Center for Church Leadership at Wesley Theological Seminary has long paid close attention to the aging and shrinking United Methodist membership in the U.S. and has urged that the church needs younger and more diverse people.
The two go hand-in-hand, said the Rev. F. Douglas Powe Jr., the Lewis Center’s director.
“If you reach younger people, you are going to reach more diverse people, which means you are going to have a more diverse congregation,” Powe said. “The big challenge is we are not reaching enough of those people.”
Gallup found that in 2020, 47% of Americans said they belonged to a church, synagogue or mosque. That’s the first time that percentage dropped below half in Gallup’s 80-decade trend. At the same time, the number of Americans who express no religious preference continues to rise.
The Lewis Center for Church Leadership at Wesley Theological Seminary has long paid close attention to the aging and shrinking United Methodist membership in the U.S. and has urged that the church needs younger and more diverse people.
The two go hand-in-hand, said the Rev. F. Douglas Powe Jr., the Lewis Center’s director.
“If you reach younger people, you are going to reach more diverse people, which means you are going to have a more diverse congregation,” Powe said. “The big challenge is we are not reaching enough of those people.”
“The findings we have for this time period is the strongest evidence to date that the homogenous unit principle, at least for Methodists, is not your best strategy for growth,” Dougherty said.
The study’s findings don’t surprise the Rev. Mark DeYmaz, author of “Building a Healthy Multi-Ethnic Church.”
“The arc of the biblical narrative bends toward multi-ethnicity,” he said. He pointed to Revelation 7:9, which promises that ultimately people of every nation, tribe and language will sing God’s glory.
“The witness of the church increasingly is tied to its ability to engage diverse people in structurally healthy, equitable, meaningful ways not only within the church but in the community,” he said.
DeYmaz is the founding pastor of Mosaic Church, a multiethnic, nondenominational congregation in Little Rock, Arkansas.
He and Freed also work together as part of the Mosaix Global Network, which strives to help congregations become multiethnic, economically diverse, culturally intelligent, socially just and financially sustainable. The two also are helping to lead United Theological Seminary’s new Mosaix House of Studies in Dayton, Ohio. The United Methodist seminary’s new doctoral and master of divinity program for multiethnic church developers is now taking applications for the fall semester.
Both Freed and DeYmaz stress that being multiethnic brings its challenges. When a church brings in new people, expect change.
For Garfield Memorial, the new outward focus entailed embracing new worship styles and new racially diverse leadership. Freed acknowledges that the changes didn’t always sit well with longtime members.
For example, he initially heard complaints from some white churchgoers that Black members’ “Amens” during sermons were distracting. Now, he said, worshippers worry when there aren’t enough “Amens” in the service.
Today, Mosaic’s outreach extends across the Cleveland area and worship services feature praise music, gospel hymns and the occasional spoken-word artist.
The Rev. Terry McHugh, Garfield Memorial’s executive pastor, said church leaders often tell those joining: “You are probably going to like 70% of what happens here. … But you have to remember your 30% is probably part of someone else’s 70%.”
Unlike the 181-year-old Garfield Memorial Church, CityWell in Durham, North Carolina, has been a multiethnic United Methodist church from its start 10 years ago.

The Rev. Crystal DesVignes is pastor of CityWell United Methodist Church in Durham, N.C. File photo courtesy of CityWell United Methodist Church.
That has meant taking a stand at times, even in protest against the government.
CityWell is part of the sanctuary movement that aims to shield immigrants from deportation. The church made national news in 2018 when Samuel Oliver-Bruno, a man to whom it had given refuge, was deported to Mexico under questionable circumstances.
Oliver-Bruno left the church for an appointment with U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services as part of the application process to stay legally, but when he arrived, plainclothes agents with U.S. Immigration and Customs Enforcement — a separate agency — arrested him. CityWell members were among more than two dozen people arrested trying to block the van taking him to detention.
Oliver-Bruno remains in Mexico after a very bad car accident, but the church still is ministering with him and his family.
CityWell’s very public witness also drew new members to join the church, DesVignes said. As of 2019, the young congregation was averaging about 200 in attendance.
The congregation also has experienced some growing pains, DesVignes acknowledged. Nonetheless, churchgoers are remaining engaged even as the pandemic forced the church to do worship and Bible studies online.
“It’s a combination of being rooted and grounded in the community, being rooted and grounded in the idea that we are not just a church we attend, but we are a family of faith, so we are siblings in Christ Jesus,” she said. “So you don’t just get rid of your family. If you have some conflict, you talk it out.”
The number of multiracial congregations in The United Methodist Church is growing, but they remain a minority. As of 2019, the denomination's General Council on Finance and Administration identified about 250 U.S. congregations as multiracial — out of a total of more than 31,000.
“Unfortunately, the church is so segregated and most people haven’t experienced this,” Freed said. “But when you do? Honestly, we have 50-year members who grew up in the all-white suburban church and they say they won’t go back.”
Hahn is assistant news editor for UM News. Contact her at (615) 742-5470 or newsdesk@umcom.org. To read more United Methodist news, subscribe to the free Daily or Weekly Digests.
Like what you're reading? Support the ministry of UM News! Your support ensures the latest denominational news, dynamic stories and informative articles will continue to connect our global community. Make a tax-deductible donation at ResourceUMC.org/GiveUMCom.